The operator's console
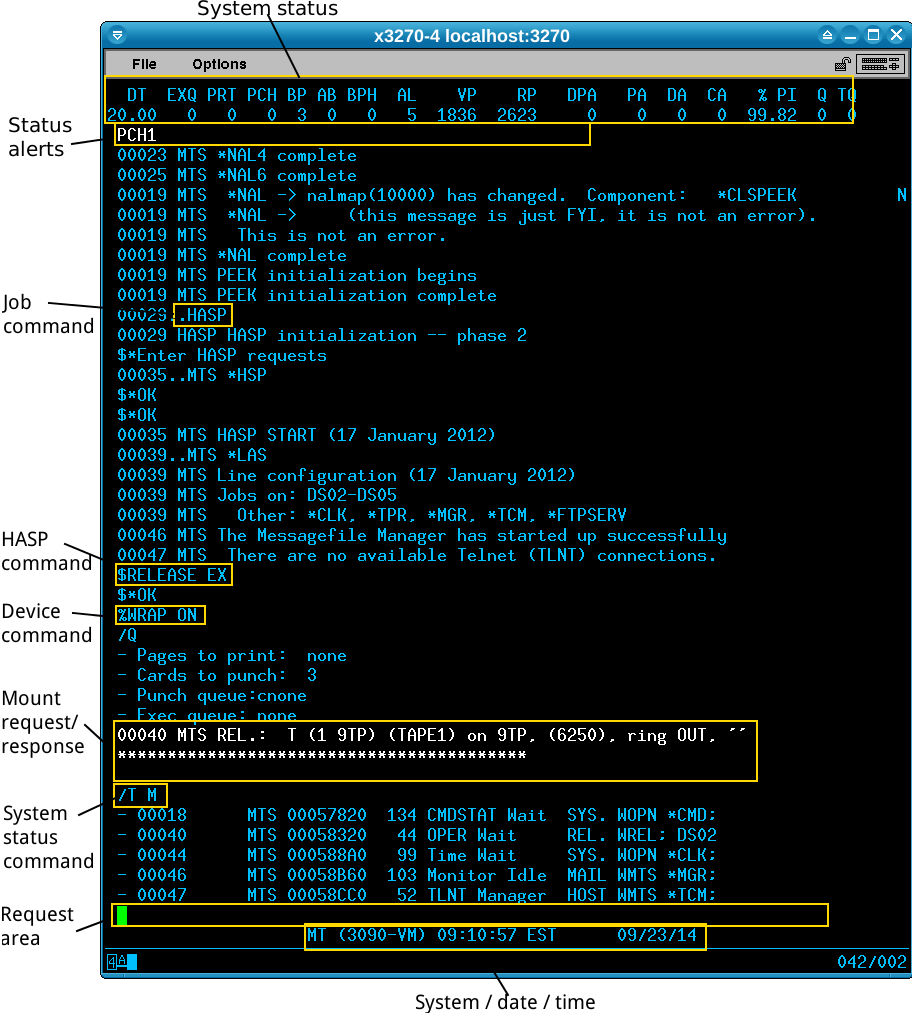
The operator’s console allows you to monitor and control your MTS system. Although you will likely use only a fraction of the features that a real operator would have used, it is worth getting to know how it works and what features are available.
This post has two sections: a quick tour of the screen, commands and keyboard controls followed in the “Further Information” section with a full list of commands.
The tour
Parts of the screen
The top two lines show a summary of the system’s status. An asterisk by an item means that the system is overloaded.
The next line, the third, will normally be blank but will show any system alerts. On the screenshot you can see PCH as the punch device is currently offline and I need to do a Hercules devinit to bring it back online. This line can also show HASP status alerts, such as when HASP has been started but batch job execution has not been resumed yet.
Taking up the bulk of the screen is the message area, showing results of commands you type and any job messages. If jobs require any input they will be bolded: on the screenshot you can see a tape mount request that needs a response.
The last but one line is the request area where you can type commands, and at the very bottom is the system name, date and time.
Keyboard
Note that the cursor position is important: in the screenshot above I can put the cursor in the line after ****** and response to the tape request, or put the cursor in the request area at the bottom to enter commands. When there are multiple input areas active, pressing Tab will move between them.
Don’t press SysRq, as this will ask for a dump tape and will exit the operator’s console program.
Types of commands
There are four types of commands that can be entered in the request area:
- Job commands, which do not have a special prefix
- HASP batch spooler commands, which start with
$ - System status commands, which start with
/ - Device commands, which start with
%
Job commands include HASP and SHUTDOWN, used in the start up and shut down process.
The GOOSE, STOP and BLAST commands, in order of severity, can be useful when dealing with user terminal jobs that appear stuck. Be careful with BLAST as it can lead to file system damage.
The MTS job has three meanings useful on Hercules
- To run MTS operator command files, eg
MTS *LAS; a list is given below. - To start an interactive MTS session on the console for any ID, without having to give a password. Type
MTS OPERthenSIGNON XXXwhereXXXis the account you want. Can be useful for a quick command but better to use a separate terminal normally. - To restart MTS on a terminal if it has been STOPed or hung up; use
MTS DSxxfor this where xx is the sequence number of the 3270 connection; this is displayed at the top of each terminal connection.
HASP commands include
$release exand$hold exto start and stop job execution$drain systemto bring the scheduler to a halt before shutdown$drain DEVto remove a device, like the punch, from HASP;$start DEVto add in back again$displayto show information about jobs
System status commands are similar to the user MTS command $systemstatus but replace that word with a /. So in userland you would do $systemstatus tasks to view a list of tasks but on the console you would do /tasks (or just /t). There are a number of additional subcommands only available on the console.
Device commands include %wrap to control line wrapping and %PF to set PF hotkey definitions.
Further information
System status columns
Key to the abbreviations in the system status area (taken directly from the D6.0A FAQ):
DT = Delta Time [time in seconds covered by the sample displayed]
EXQ = Execution Queue [number of batch jobs waiting to execute]
PRT = Print Queue [number of jobs waiting to print]
PCH = Punch queue [number of jobs waiting to punch]
BP = Batch Preferred [the number of batch jobs the system would
"like" to be running]
AB = Actual Batch [the number of batch jobs actually running]
BHP = Batch per Hour [average number of batch jobs completed per hour]
AL = Active lines [MTS terminal sessions]
VP = Virtual Pages
RP = Real Pages
DPA = Drum Pages Available [pages available on the high speed
paging devices, rather than disk]
PA = Paging Activity [paging I/O operations per second]
DA = Disk Activity [disk I/O operations per second]
CA = Channel Activity [channel I/O operations per second,
includes DA and a portion of PA as well as
other I/O operations]
%PI = Percent Processor Idle
Q = Global CPU Queue [jobs waiting for the CPU]
TQ = Tape Queue [MTS jobs waiting for one or more tapes
drives to become available]
Job commands
A summary of the job commands available is given below. Full documentation can be found starting from page 81 in the Operator’s Manual.
BLAST- forcibly kill a job if STOP will not kill it.BROADCST- send a message to terminals attached to the systemDIS- display contents of memory locationsDMGRSTAT- manage disksFLUSH- clear requests from HASP for I/O for a device (after draining)GOOSE- simulates sending an ATTN to a taskG11- g11 3211 printer configHASP- start the spoolerHASPLING- hasp subjobs, not started by handINIT- initialize system, not started by handIT- list networksJOBDUMP- dump a job core memory to tapeJOBS- list job statusMOD- change a location in memoryMTS- start an MTS taskOFFLINE- mark a device as logically offlineOK- determine how jobs that terminate successfully display to the consoleONLINE- mark a device as logically onlineOPERATOR- start the operator consolePDP- initiate the Paging Drum ProcessorPDROP- remove paging devicesPGET- set up extra paging devicesPN- printer train configQN- printer train configSE- print device tableSHUTDOWN- shutdown the (terminal) part of the systemSIGNONM- print a sign-on message to all users before they sign onSOFTCHK- control the recording of soft (recoverable) machine checksSTARTUP- reverse the effects of shutdown on a terminalSTAT- collect system statistics to a tapeSTATSW- dynamically change the parameters that a STAT job is usingSTOP- kill a jobTABLMOD- display or modify information in the shared file tableTASKS- display status of running tasksTMTS- run a task using the test version of MTTN- printer train configT11- printer train configUNITS- display config of channels, control units etc
MTS operator’s files
All commands below need to be run by MTS and prefixed with *, eg MTS *BBS. Many (most?) of these will not be of use on Hercules, eg those involving networking or plotting hardware. Full documentation starts from page 161 in the Operator’s manual.
AAS- Starts network tasks AA21 - AA29ABS- Starts network tasks AB10 - AB6FADS- Starts network tasks AD10 - AD73AES- Starts network tasks AE10 - AE73AFS- Starts network tasks AF10 - AF6FANS- Starts network tasks AN10 - AN6F AND DSNBBS- Babysit program to watch for user ID signonBDL- Dump, reload PCP “AB”CCD- To Defer PlotsCCL- Initializes Plot TapesCCP- Dump Plots To TapeCCR- Reset/Startup PDP-11 “C”CCS- Normal Startup PDP-11 “C”CCT- Length Of Plot SessionCDL- Dump, Reload Data Conc. “C”CHK- Checks For Offline EquipmentCLB- Retrieves Label From Tape And Inserts It In Tape CatalogCLK- Starts Automatic Job Scheduling ProgramCLN- Cleans Up machine check and unit check Info.CLO- Reloads DC “C”-No DumpCLR- Restarts Job Scheduling ProgramCMB- Combine Statistics TapesCMD- Command StatisticsCPW- Change Password To UnknownCTD- Check Disks After PMDCS- Starts Data Concentrator CDDL- Dump And Load Primary Communications Processor ADDLG- Logs Disk ErrorsDLO- Reloads PCP “AD”-No DumpDMP- Initiates BATCH Job To Print DumpsDRN- Drains HASP RemotesDSD- Runs DASDIDSK- Add,List,Delete DisksDSN- Start User HASP Display - NUBSDSO- Amount Free File SpaceDSP- User HASP Status Display - CNTRDWB- CMDSTAT + Unit Checks To TapeEDL- Dumps & Reloads PCP AEELO- Loads Primary Communications Processor AEEUP- Enables terminals on EE01 SCP in the East Engineering buildingFIR- Names & Ph. #s Of Fire FightersFIX- Update CCID Accounting RecordFLB- Check Tape LabelsFSC- Make Copies Of File Save TapesFSM- File Save MergeHGS- Show 10 Jobs With Most CPU, DSK I/O etcHLB- Force Access To UB Host Through Host LocatorHLG- Hasp Log CollectionHLM- Force Access To UM Host Through Host LocatorHPS- HASP StatusHSP- Normal HASP StartHUH- Merit + Concentrators, State Of*IG.SHUFFLE- Summarizes*IGUsageINI- .System InitializationITX- Intertask Communication Test-UMMPS JobsLAR- Reset Line Adapters-1270LAS- Start 1270 And Misc JobsLBH- Tape Labeling (non-catalog)LBL- Tape Labeling (catalog)LIM- Time Remaining-Batch JobsLMT- Short Version Of MSSLRL- Info. About Last IPLMNS- Normal MERIT StartupMSD- Set Time-Date Merit CCsMSG- Cleans Up $Message SystemMSS- Tape Usage HistoryMUP- Current State Off MERIT ComputerNDL- Dumps & Reloads Primary Communications Processor ANNST- NAS-Manipulation Of Name Address SpacesNUP- Enables Terminals On NUBS SCPs & Job Status MonitorOOT- Controls NTM On UB & UMPAG- Tests Paging DevicesPLB- Prints Identifying Info. About Plot TapeP16- Starts 16 PAG JobsRCP- MTS S-8 CardsRES- File Save: Status & RestorationRHB- Releases & Holds HASP Rate ClassesRIP- PN Ripple PrintRST- Restores FilesRSV- Reserves Disk DrivesSAV- Daily File SaveSDB- PCP Shutdown Msg. & DisconnectSDM- D.C. Shutdown Msg. & DisconnectSFT- Starts SOFTCHK-Checks For Soft MCHKSSTA- Saves Statistics On TapeSTI- Checks Condition Of Statistics Work FileSVS- Special Large, Weekly Type FilesaveSVW- Weekly File SaveTNR- TN Ripple PrintTPD- Tape & Tape Unit DiagnosticsTPS- Displays Amount And Type Of Free Tape UnitsTSH- Add Tapes To Or Remove From UNSP:TAPESHARETSN- Weekly Full File Save Slave StreamUNU- Enables Terminals On NUBS & UNYN SCPs & Job Stautus Monitor
HASP commands
Once the spooler has been started by running the HASP job, there are a number of commands available to control spool execution. Full details in the HASP manual.
$ACCEPT [RMID] modifier- define what output each site can accepr$ALTER JOB n PRIO +or-M | DEFER | LOW- alter job priority$BACKLOG [log]- display job backlog$BACKSPACE dev n- fix paper jam by restart print from 2 pages back$DELETE dev n- terminate the current job running on devicedev$DELETE JOB N- terminate job numberN$DISPLAY JOB n- display info about jobN$DISPLAY PRIO JOB n- display priority of jobN$DISPLAY RMTS|REMOTE NAME|REMOTE NUMBER [LOG]- display status of remote dvices$DISPLAY {UNIT Dev N | UNITS [LOG]}- display I/O unit status$DRAIN dev n- Allow current job on deviceNto finish then remove device from spooler.$DRAIN SYSTEM- Allow all current jobs to finish but do not execute any new jobs$FORMS Paper,devn- Define papet type on device$HOLD *...*- Hold access to the pseudodevices*PRINT*, *PUNCH*, *BATCH*$HOLD EX- Hold execution of batch jobs (but allow printing/punching)$HOLD JOB n or ALL or LOW or DEFER- Put a hold on batch jobs$INTERRUPT dev n- Interrupt the printing of the job on deviceNand put it back on the queue,$LIST- Define level of log messages to be printed.$LOCATE JOB n- Find out execution info for jobN$LOCATE User CCID- Find out execution info for jobs from userCCID$LOGIO ON/OFF DEVn- Log all message for a device$LOG MESSAGE- Send a message to the log file$NEWHASPLING dev n- Start a new HASP internal job$PASSWORD- Set password for remote station$QUE [MAIN]- Show queue information$REFUSE [RMID] modifier- define what output each site can accepr$RELEASE *...*- Release access to the pseudodevices*PRINT*, *PUNCH*, *BATCH*$RELEASE EX- Release execuion of batch jobs$RELEASE REMOTE JOB n or ALL or LOW or DEFER- Release jobs put on hold$REPEAT dev n- repeat printed output for job printing to deviceN$RERUN JOB n- Terminate jobNand place back on the queue$RESTART dev n- Terminate job running on deviceNand immediately rerun$RMSG (nn Or Rmid Or All) Message- Communicate with remote stations$ROUTE TYPE for-id to-id- Define routing for output of job$SETUC [RMID] On|off- Set upper-case option for remote stations$SIGNOFF- Stop a remote terminal after completion of current read/punch$SPACE dev n- Stop carriage control and single space output for job running on deviceN(useful for runaway print jobs)$START modifier dev n- Add a device back under HASP control$START SYSTEM- Start HASP operation (done as part ofMTS *HSP)$STATUS [log] N- Show status of deviceN$STOP dev n- Stop execuion of current job on deviceNand remove device from HASP$TEST- Check console is working
System status commands
Full documentation can be found starting from page 456 in the Operator’s Manual.
/ALTER- Change system scheduling parameters or virtual memory/AREAL- Change real memory contents/ATTN- Send attention interrupt to a task/BLAST- Force kill a job/DEVICE- Display info on a device/DISPLAYLOCK n - Display locks, eg stat job lock/DISPLAY- Display predefined variables/DREAL- Display real memory contents/FIO- Force a fake I/O interrupt/JOB- List details of jobs/KILL- Kill a job/LOAD- Print load info, like the top 2 lines of the operator console/OPER- Print output of operator’s console or send command to console/QUEUE- Display queue status/SCREEN- Display job status in TV screen like format/TAPEQUEUE- Control and list the tape queue/TASKS- Print task information/USERS- Prints user information
There are also some synonyms, eg /MODIFY for /ALTER.
Device commands
Like on MTS terminals, device commands start with %, but the set of available commands is different. Full details are on p331 of the Operator’s Manual.
%3270 devn- switch console device to bedevn%ACCEPT ALL|job- control if messages are displayed by jobs%EMPTY- Empties the screen.%FAST- Switches terminal into fast mode; not of use on Hercules.%IGNORE jobn- control if messages are displayed by jobs%PF?- Lists PF key definitions%PFn=def- Redefines program function key PFn to bedef%PTR devn- Switches the console printer device%REFRESH- Makes sure that the screen is up to date.%RESTART- Switch back to main terminal from backup.%SLOW- Switches terminal into slow mode; not of use on Hercules.%WRAP ON|OFF- Control line truncation